Who we are
The Sustainable Rural Development in the Caatinga (PRS Caatinga) is an initiative resulting from an international cooperation agreement signed between the governments of United Kingdom and Brazil. It is financed by the United Kingdom’s International Climate Fund in cooperation with the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), with the Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Supply (MAPA) as an institutional beneficiary. The execution of PRS Caatinga is carried out by the Brazilian Foundation for Sustainable Development (FBDS).
FBDS
The Brazilian Foundation for Sustainable Development (Fundação Brasileira para o Desenvolvimento Sustentável – FBDS) is a nonprofit organization differentiated by its network with the scientific community, international finance agencies and national corporations.
FBDS considers and structures projects and partnerships on the subject of sustainable development by means of an organization which integrates the forefront of know-how with management capacity. Its Board of Trustees combines solid corporate experience with thorough technical-scientific know-how, adding value to the Foundation’s institutional positioning and reinforcing its ethical and professional credibility.

It was founded in 1992 and its mission is to disseminate the best environmental and sustainability practices and influence its target publics by means of generating know-how, contributing to the formulation of public policies and carrying out consulting projects.
Our objectives
"To mitigate greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions,
reduce poverty and increase the income of small and medium-sized
farmers in the Caatinga biome by promoting the adaptation of
low carbon technologies for agriculture."
Low carbon technologies
Low carbon technologies for agriculture are a set of techniques designed to improve productive activities, redirecting them towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions, preserving natural resources, and maintaining or expanding agricultural production in a sustainable manner.
In Brazil, the low carbon technologies for agriculture were developed from experiences in other biomes. Therefore, we are building, in a pioneering and collective way, dialogues, and strategies for their adaptation to the specificities of Caatinga (dryland).
One of our strategies is to strengthen local productive arrangements by linking their productive activities to the climate agenda in order to reduce vulnerabilities, promote environmental preservation, and improve the income of rural producers.
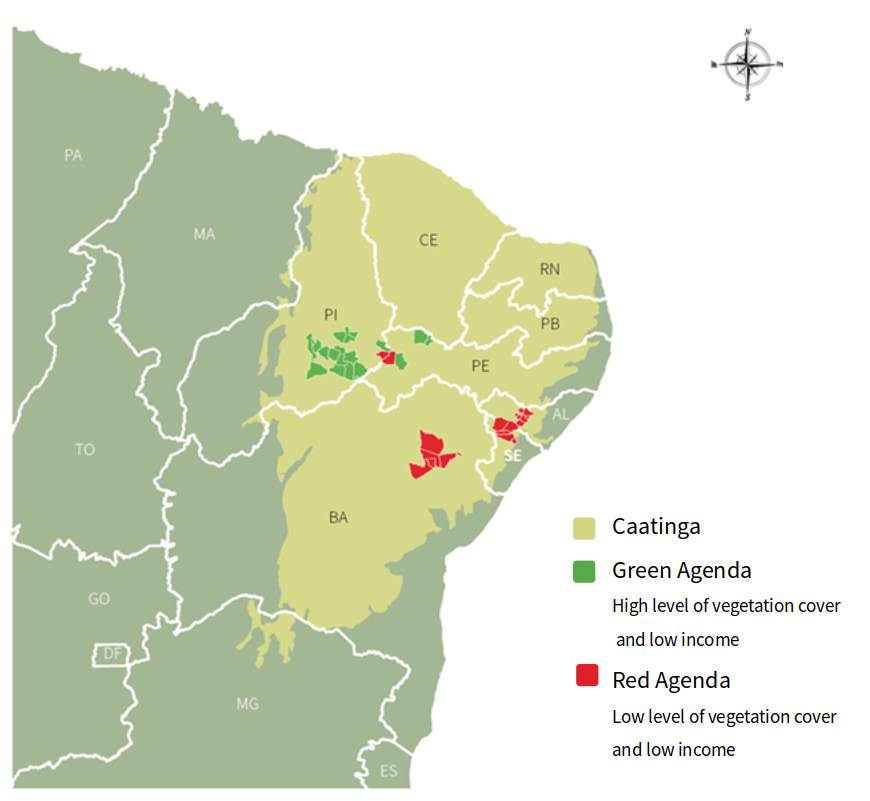
Field area
The Caatinga biome is located in Northeast Brazil, the region with the lowest Human Development Index (HDI) in the country. It concentrates 18% of the country’s poorer rural population and 10% of the poor national population. Near 60% of the municipalities are under the poverty line of US$1,25 per capita per day.
Agriculture plays a key role in the Caatinga biome. Nearly 12% of Brazil’s population live in the region and depend on agricultural activities. Approximately 32% of the 5 million farms in Brazil are located in the Caatinga. Traditional agricultural practices, such as the use of slash and burn and overgrazing, are common, causing land degradation and increasing desertification. The native vegetation of the Caatinga has been transformed by deforestation, with geoprocessing monitoring indicating that 45% of the biome has been deforested and degraded.
As a result, the Caatinga has become the third most degraded biome in Brazil after the Mata Atlântica and the Cerrado and will be the more severely impacted biome in Brazil by the change in temperature. On the other hand, the studies also demonstrate that agroforestry systems in the Caatinga have the potential to store approximately 11,72 tons of CO2.
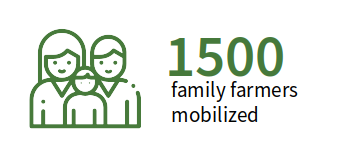
Goals







Main strategies
PRS Caatinga intends to achieve its objectives by:
Knowledge Generation on the Caatinga Biome
- Support studies to expand the knowledge and understanding of the Caatinga biome. Results from these studies will contribute to the development of a capacity-building program that will be made available to the existing local technical assistance services and organizations, with the intent of updating their concepts and practices on low carbon rural technologies.
Sustainable Low Carbon Productive Arrangements
By strengthening capacities of local technical assistance providers:
- Offering updated technical assistance to small and medium-size local farmers in adopting climate-smart technologies; and the provision of training and technical assistance to farmers and rural organization: training and technical assistance to farmers and their organizations to raise their awareness and knowledge about low carbon technologies and to support their adoption of these technologies.
- Supporting value chains and access to markets: strengthen the capacities of small farmer organizations through the financing of collective benefits, such as water storage, seedling nurseries, small-scale storage facilities, and tools for compost production.
Creating a Sustainable Legacy in the Caatinga
- Designing a Caatinga facility/fund: a financial mechanism, in form of a fund or facility, which would provide grants and credit to small and medium-sized farmers, aimed at ensuring project sustainability after its completion.
- Engaging with strategic stakeholders: promote a network of associations, cooperatives, educational institutions, government and non-government institutions and players in the Caatinga, involving them in the project to create multiplying actions aimed at scaling up project results.
- Disseminating knowledge and best practices: organization of workshops and seminars to share project results with academia, government and private sector, exchanges with technical and scientific institutions, and development of an online platform.
Contact
To learn more about PRS-Caatinga, please contact us.

prs.caatinga@fbds.org.br

@prs.caatinga